In last week’s article we covered how our environment, namely pollution caused by radiowaves, has been linked to cancer. Radiation is a form of light that we cannot see, yet our eyes and bodies do perceive and absorb radiation through our cells.
This week’s piece will focus on light that we can see, namely light from the sun, and blue light from our devices and LEDs.
Skin in the Game
Melanin is a pigment that we all have, and its role goes well beyond determining skin and eye color. Melanin helps protect our skin against the effects of UV and blue light on the skin’s surface by actually being able to absorb UV.1
Here’s the kicker: we must expose ourselves to the sun to produce melanin. We’ve all heard that UV light can cause cancer, however most of these studies were conducted in labs, and not under full-spectrum sunlight. The infrared (IR) light, along with other spectra, balance UV throughout the day.
In un-tanned individuals, melanin pigments are found only in the base layer of the skin, while in tanned individuals it’s distributed deeper and in higher concentrations.
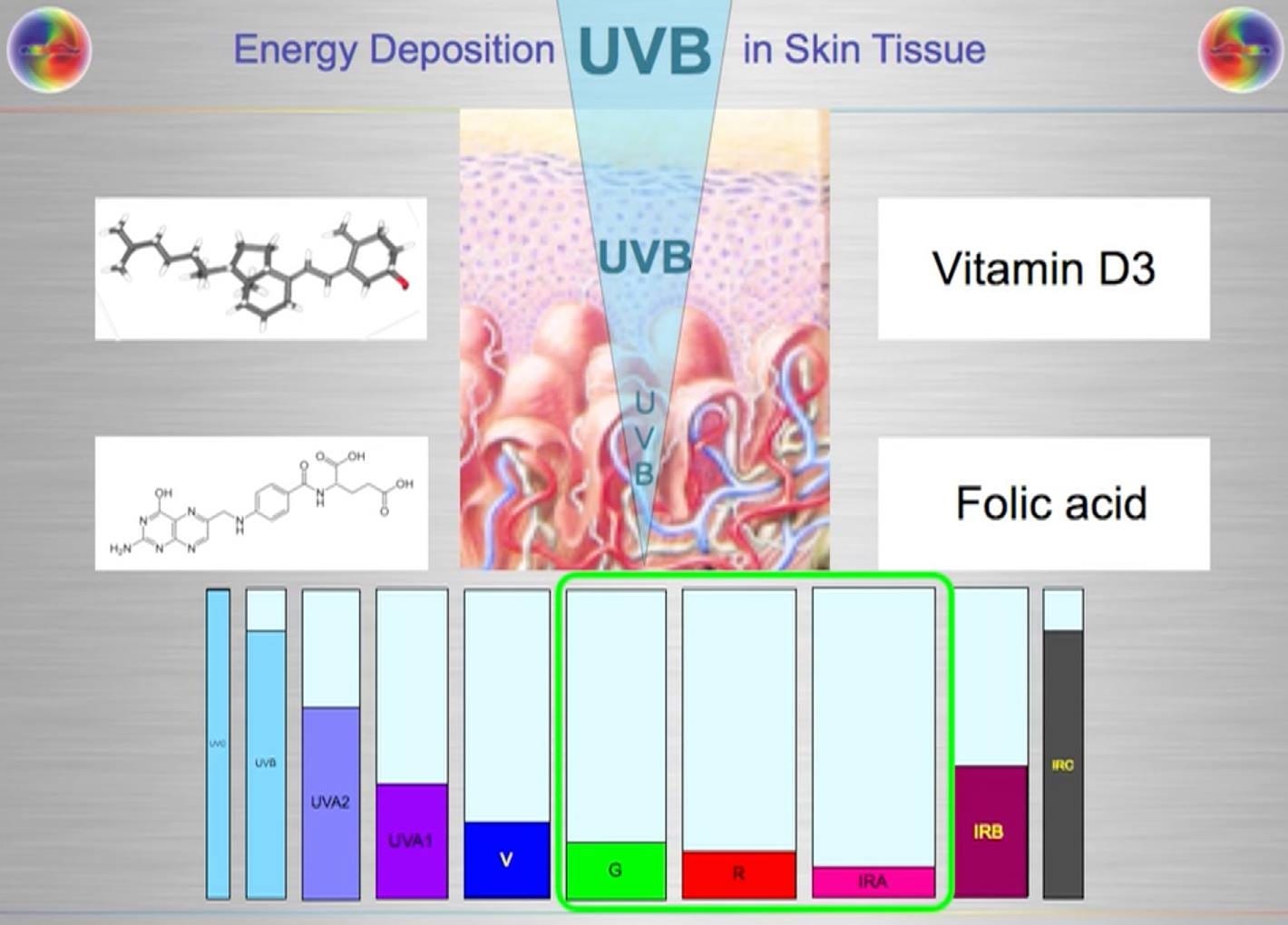
Recent investigations have shown how when melanin is distributed deeply in our skin, the amount of UV radiation that reaches living cells in the epidermis (outer layer) can positively affect folate and B12 levels and repair the DNA in our cells.2 3
However we must gradually build up this protection by exposing ourselves to the sun throughout the year. UV-B radiation, which is most prevalent during the hours of 11am-1pm, penetrates more deeply into our skin and can have a greater potential for positive or negative health effects.
If we have less melanin due to being inside throughout most of the year, and under blue light (which destroys melanin)4 our tendency for a sunburn and inflammation will be increased.
If we’ve built up our melanin stores gradually, we’ll not only be able to be outside longer, we’ll also be able to quell inflammation and support healing throughout our body. Additional research shows that melanin may contribute to the reduction of inflammation in the body, and may prevent injuries to the liver.5
Melanin is able to transform 99.9% of sunlight into heat, which is energy our cells can use. This heat greatly reduces cancer risk.6
I wear my sunglasses at night
Melanin is also found in the base layer of our eyes, known as the RPE (retinal pigment epitheleum).
"Sunglass marketing ads have trained us to wear sunglasses whenever we go outside, ostensibly to protect our eyes from damaging UV rays.
However, melanin—which gives your eyes their blue, hazel, green or brown color—already protects them from UV rays. In fact, the human eye has evolved to deal naturally with sun exposure through antioxidant protection by melanin, as well as other antioxidant-defense systems based on glutathione,
I believe it’s crucial to get adequate sunlight exposure to the eyes, not just for the sake of eye health but also because critical nuclei in the brain stem make good use of light that enters through the eyes.”
-Stephanie Seneff, PhD
There has been extensive research on how blue light can harm our vision and impair sleep, especially at night. Harvard researchers showed how blue light impairs the production of melatonin, which is cancer-protective. Blue light was shown to suppress melatonin for about twice as long and shifted circadian rhythms by twice as much (3 hours vs. 1.5 hours).7
“Blue light at night throws our biological clock—the circadian rhythm—out of order. Worse, research shows that it may contribute to the causation of cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and obesity."8 - Harvard: Blue Light Has A Dark Side
Chemists at the University of Toledo conducted a 2018 study9 showing how blue light destroys our retina permanently:
“Photoreceptor cells do not regenerate in the eye. When they’re dead, they’re dead for good. The retinal-generated toxicity by blue light is universal. It can kill any cell type.” - Kasun Ratnayake, PhD
On a personal note, I wear computer glasses throughout the day, which are tinted and block most of the blue spectrum. At night I wear amber-red glasses which block all of the blue spectrum. However I don’t advise wearing red glasses during the day, and especially if you’re driving, as our melatonin begins to kick in after two hours and makes you sleepy. Here’s a link.
Brain cancer not caused by cell phones?
According to the highly-touted INTERPHONE study10 conducted by the World Health Organization, the results are inconclusive. However I read the study, and do you know what I found?
The research didn’t look at those with high cell phone usage.
“That’s like doing a study on obesity looking a people that are slightly overweight.” - Jack Kruse, M.D.
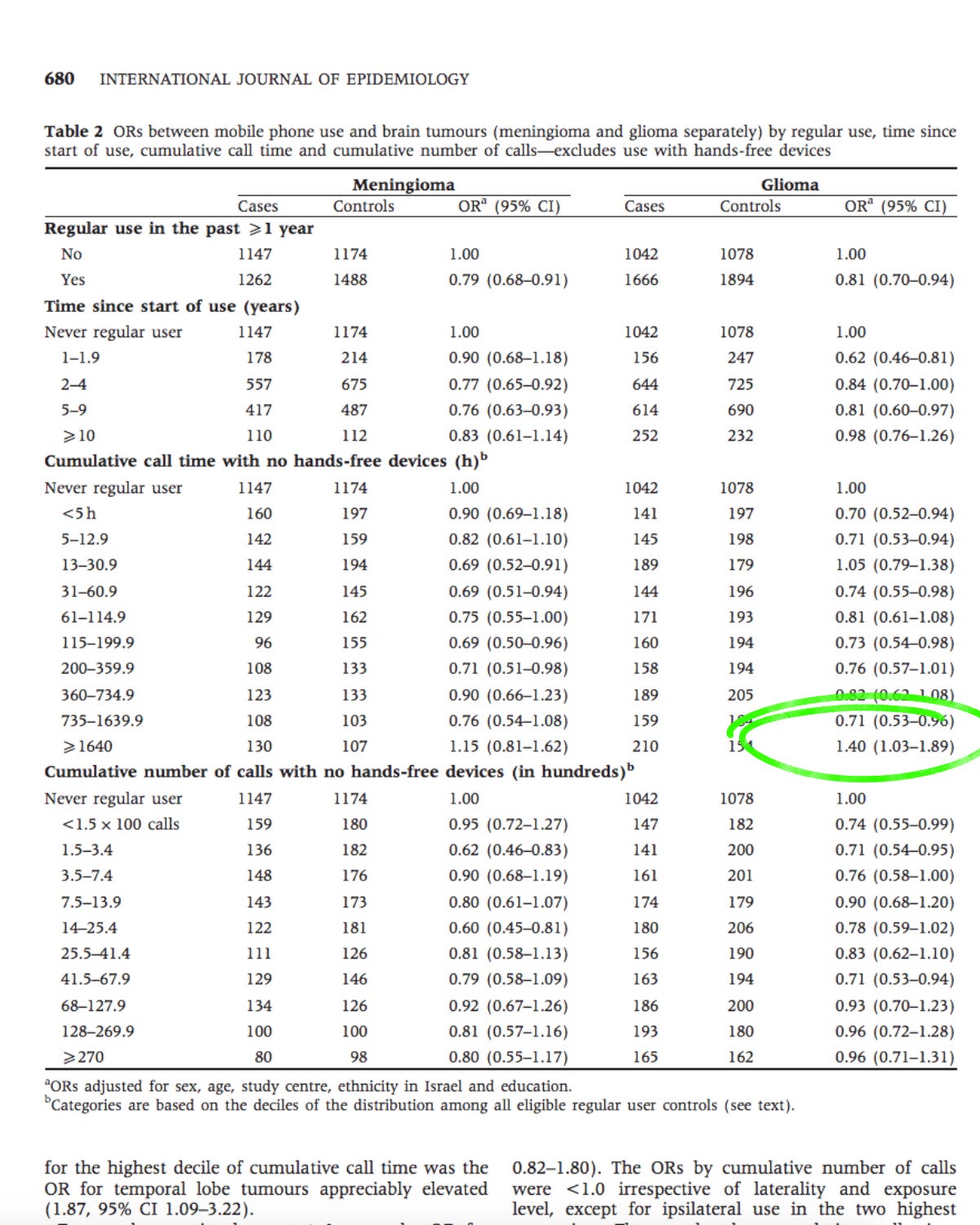
The parts of the study that did look at high cell phone users found a doubling and up to a quadrupling of tumors. You’ll see below where I circled in green, the odds of having brain cancer doubled once you were a heavy cell phone user.
Participants who used cell phones the most were shown to have 4x the odds of developing brain cancer. (OR= Odds Ratio):
There’s also a slight conflict of interest as some of the study was backed by the Mobile Manufacturers Forum (MMF) and Groupe Speciale Mobile Association (GSMA) - the people who sell us cell phones!
I would also mention that the participants who contracted brain cancer had an average lifetime total of only 75 hours. We all know some people who are on their phone 75 hours a week, let alone 75 the past 10 years.
The conclusion of the study? Overall, no increase in risk in brain caner was observed with use of mobile phones.
In my opinion, this type of research is by design, only helping rake in the cash for Apple, Verizon, and Google.
Many neurosurgeons such as Jack Kruse, along with scientists such as
and others are sounding the alarm.