Many of us fear the fallout from the wireless radiation of 5G and cell towers, yet we’ve forgotten the most commonplace predator in our lives.
Here’s what you’ll learn in this article:
1. How life cycles are similar to light cycles
2. How does blue light affect health: the Big Picture
3. Impact on melatonin
4. Why blue-blocking glasses dont’ save us completely
5. Impact our hormones
6. How liver detox is disrupted
7. How children absorb blue light
8. How blue light contributes to brain disease
9. Environmental impact
One of the most intense forms of EMF (electromagnetic field) we’re subject to in our modern society is blue light. Yes, light is EMF.
You can learn about light and EMF basics here:
Life cycles are light cycles
This light comes not only from our devices, televisions, and LED bulbs, but is also present in sunlight. Blue light from the sun can even boost our immune system by energizing infection-fighting T cells.1
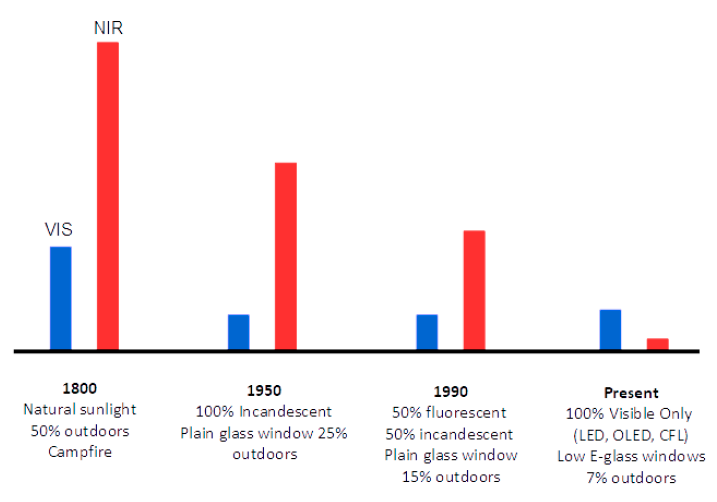
The solar spectrum provides a balance of light, whereas the spectrum of our indoor generation’s LEDs and electric lighting ruins this delicate equilibrium of light that forms the foundation of our metabolism.2
Consider prey and predator as a couple. When predator eats prey, this has a positive effect on the eater, and a negative effect on the eaten animal.
The negative effect on predators when they eat prey: less prey animals prevents uncontrolled growth of the predator's population. This stabilizes the population sizes of both groups when they are coupled.3
Red light helps us relax and regenerates our nervous system, while blue light keeps us energized and primes our fight/flight response.
“Blue and red light in the sun are like predator and prey...they each perfectly balance one another. But modern artificial light has 4 times the amount of blue and no red. This destroys the coupled cycle.”
How does blue light affect health?
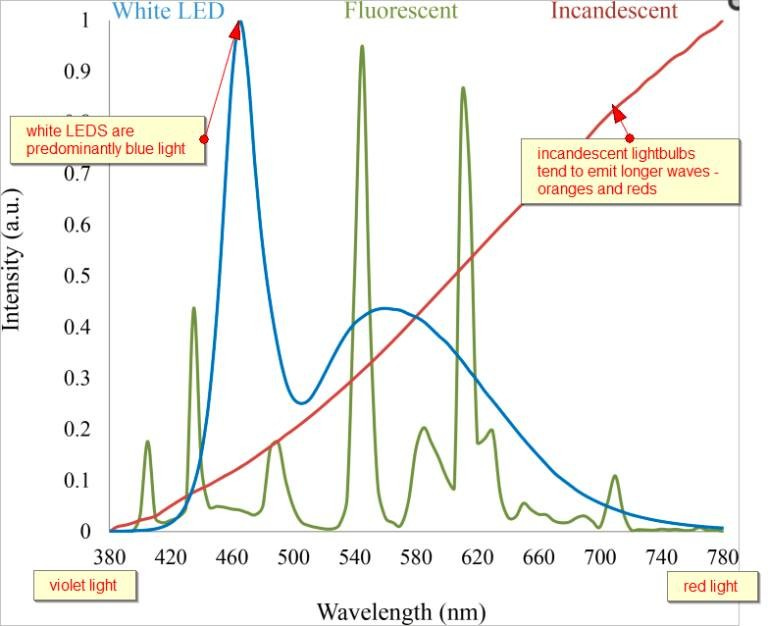
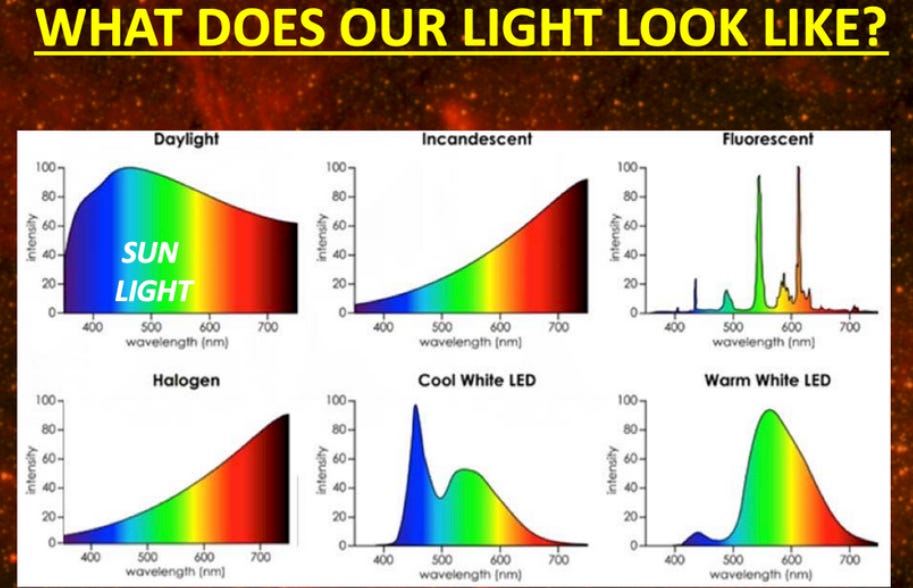
The blue light that is emitted from our screens is a shorter wavelength of approximately 450nm (nanometers) as compared to incandescent bulbs which can run into the infrared range (IR) of 700nm.
Why does this matter?
Shorter wavelengths take longer to pass through our cells, and this light contains more cellular information for our bodies to process.
Longer wavelengths from IR light pass through more quickly. You can see an illustration of this effect on the video I posted here: “What You Need to Know About EMF”.
You may not be able to tell, but the blue light that is emitted by our phones is pulsed, which is harder for our eyes to process. In order to understand why this type of light can be so harmful, we first must appreciate how light evolved to be beneficial to humans throughout our history.
Before the advent of electricity, societies lived by candlelight (infrared source) and under the full spectrum of the sun. Almost half of the solar spectrum is comprised of infrared light, which regenerates our body by increasing melatonin stores in our skin, eyes, as well as allowing our mitochondria to produce energy efficiently.4
Back to the concept of balance. We’ve heard that UV light can cause skin cancer. Yes, alone it can. However, did you know that most of the data that links the sun to skin cancer comes from studies done indoors using UV light from man-made sources and not the sun.5
We need UV, as well as the infrared spectrum for our bodies to work. Amino acids such as tryptophan absorb light in the UV spectrum of 210nm, and hormones like serotonin also absorb UV light at 337nm. Our mitochondria, which generate energy for our metabolism, love infrared light at 620-680nm.
What are we absorbing today?
Here’s the big picture:
Notice how much more of a rich, full spectrum was available for our bodies before the advent of the light bulb?
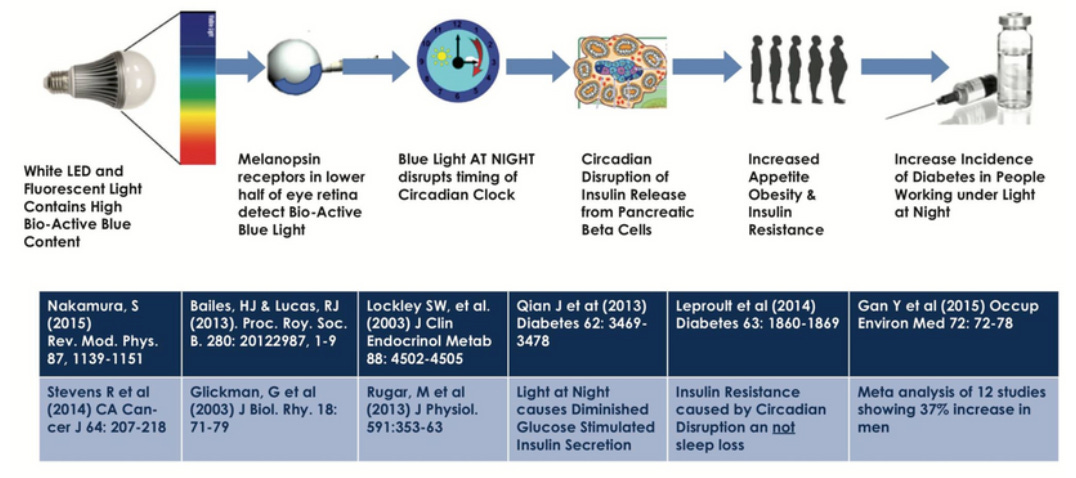
Blue light destroys melatonin
Many researchers, including those from Harvard6, have shown that blue light at night, or even any artificial light at night (ALAN) destroys melatonin. Melatonin is a hormone that our bodies secrete at night so that we can regenerate, repairing all of the damage we've done during the day, as well as eliminate mitochondrial waste products through a process known as mitophagy.
Many of us think of melatonin as the “dark hormone.” Light at night suppresses melatonin. However what many don’t know is that light during the day is what regenerates the melatonin stores in our body. We actually have two different types of melatonin. One type is secreted by the pineal gland of our brain, and the other is called subcellular melatonin, and stored in our skin as we expose ourselves to sunlight throughout the day.7
Our bodies typically need about two hours of total darkness to begin secreting melatonin at night, and it takes about four hours for melatonin secretion to peak. This means that if you look at your phone at 10pm, you won’t start the process of falling asleep in earnest until midnight. Since melatonin still requires time to run its course through our bodies, you may still have some in your system when you wake up, feeling groggy as a result.
Blue-light blocking glasses don’t save us completely
Proteins are the building blocks of life, and give our cells messages on how to function. The study of epigenetics, or how our environment triggers certain genes to turn on or off, maintains that these on/off signals are mediated by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Opsins are such a protein.
Our blue-light detectors: melanopsins
Opsins are light-sensitive retinol (vitamin A) proteins, and until 2017 was thought only to exist in our eyes. We now know that our skin and fat also contain this photoreceptor.
Melanopsin is particularly sensitive to the absorption of blue light (435nm - 480nm) and will communicate this light frequency to our central clock: the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which dictates our circadian rhythm.
Disclaimer: I do wear blue-blocking glasses at night.
Our eyes are more densely packed with mitochondria than our skin, so they can be more acutely affected by light.
God did give us only two eyes, so any time I can protect them I will. I’ll even jog backwards at sunset when I see other cars coming my way with their blue beaming rays.
Our Master Clock, the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)

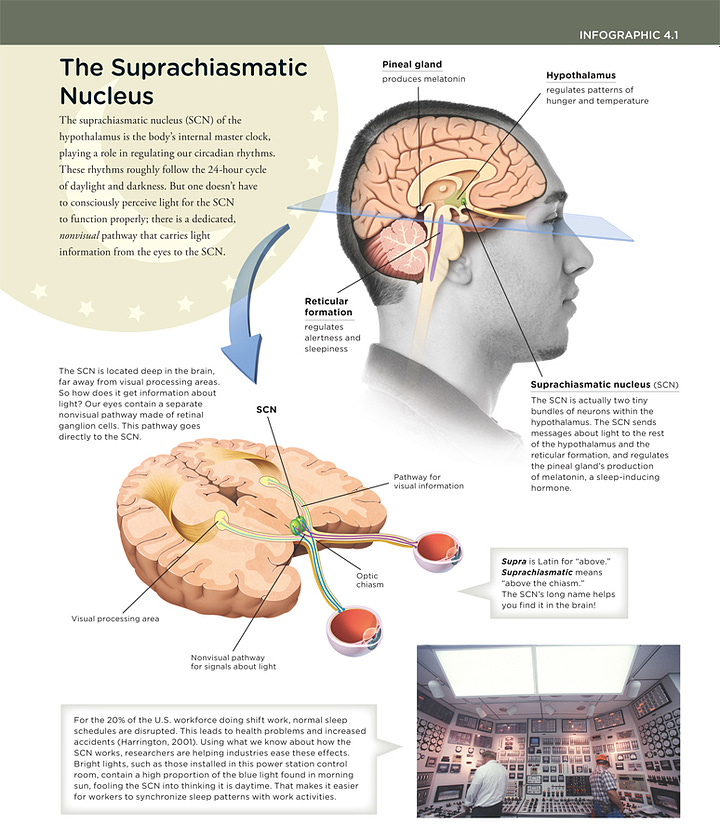
Our circadian rhythms drive our metabolism, and each of us even has an invididual rhythm that dictates how well we can digest food at certain times during the day.
When these rhythms are thrown off, a cascade of effects occurs, which can lead to cancer, autoimmune disease, or diabetes as in the example below:
Blue light chronically elevates blood glucose. When blood glucose is chronically elevated by your blue light-toxic environment, red blood cells cannot deliver oxygen well to mitochondria.
If melanopsin is also found in our skin, do you still think staying up watching Netflix until midnight with your biohacking blue-blocking glasses is a good idea?
“Melanopsin is the blue light detector of light that links to the leptin hormone in our fat. The interaction between melanopsin and leptin allow the hypothalamus to know the correct energy balance in the body. This process also controls the levels of melatonin in the body, which control the efficiency of apoptosis (programmed cell death) and optimizes tissue level energy and information transfer to and from the brain's hypothalamus, operating tight control over the molecular clock functions in the body.”
-Jack Kruse, M.D.
Basically, melanopsin not only regulates the amount of melatonin that will ultimately be released from our pineal gland at night, it is also the key driver in setting our circadian rhythms and sleep patterns.
Melanopsin regulates our sleep the following two ways8:
The circadian mechanism, which determines the optimal time for sleep.
The homeostatic system, which keeps track of how long the body is awake and asleep, triggering “sleep pressure” when the body suffers from sleep deprivation.
Melanopsin is also our eyes’ dimmer switch, as it allows the pupillary reflex to work during the time of sunrise and sunset. If you’re a romantic like me and like exploring unique vistas to see the sunset, melanopsin is what helps you find your way back home.
When we expose ourselves to excessive amounts of blue light, we not only deprive ourselves of quality sleep, we desensitize melanopsin so that we no can longer see as well in low-light environments.
When melanopsin signaling is altered in the central nervous system for any reason at all, mammals lose the ability to catch up on sleep permanently.
-
, M.D.Blue light affects our hormones
When we absorb high-energy EMF (electromagnetic fields) in the form of blue light, we also destroy our stores of retinol, or vitamin A.
We need vitamin A to make:
thyroid hormone
progesterone
testosterone
growth hormone
Once our melanopsin receptor is desensitized, the enzymatic pathway of vitamin A can be irreversibly damaged.9
Do you still think that you can supplement or eat your way out of a highly toxic blue-lit environment?
Another way our hormones are affected by blue light is cortisol. Cortisol is a stress hormone we use in our fight/flight response. It’s meant to be fast-acting, and have a resolution once we’ve run from the lion. However in our modern day, we’ve become chronically stressed at a very low level. This can create a condition known as hypercortisolism (Cushing’s syndrome).
Anytime cellular stress is high, which includes stress from excessive blue light- it also forces an all-important prohormone pregnenolone to be switched to cortisol production.
What does this mean?
Many of our hormones such as DHEA, androstenedione, Vitamin A, D, testosterone, estrogen, and aldosterone, are made from pregnenolone. When its production is disrupted, all of these hormonal levels fall dramatically as a result.
When cortisol is up, melatonin is also down.
These types of hormonal imbalances can lead to all types of mood disorders, cancers, and autoimmune disease.
Blue light disrupts detox
Our livers detox through the cytochrome p450 enzymatic pathway.
Why is this relevant?
This "p" enzyme was given its name because its absorption of light peaks at 450nm10, which is the same wavelength as blue light.
An excess of this light disrupts liver metabolism.
When we have melanopsin dysfunction, cytochrome p450 no longer works effectively.
Children absorb more blue light
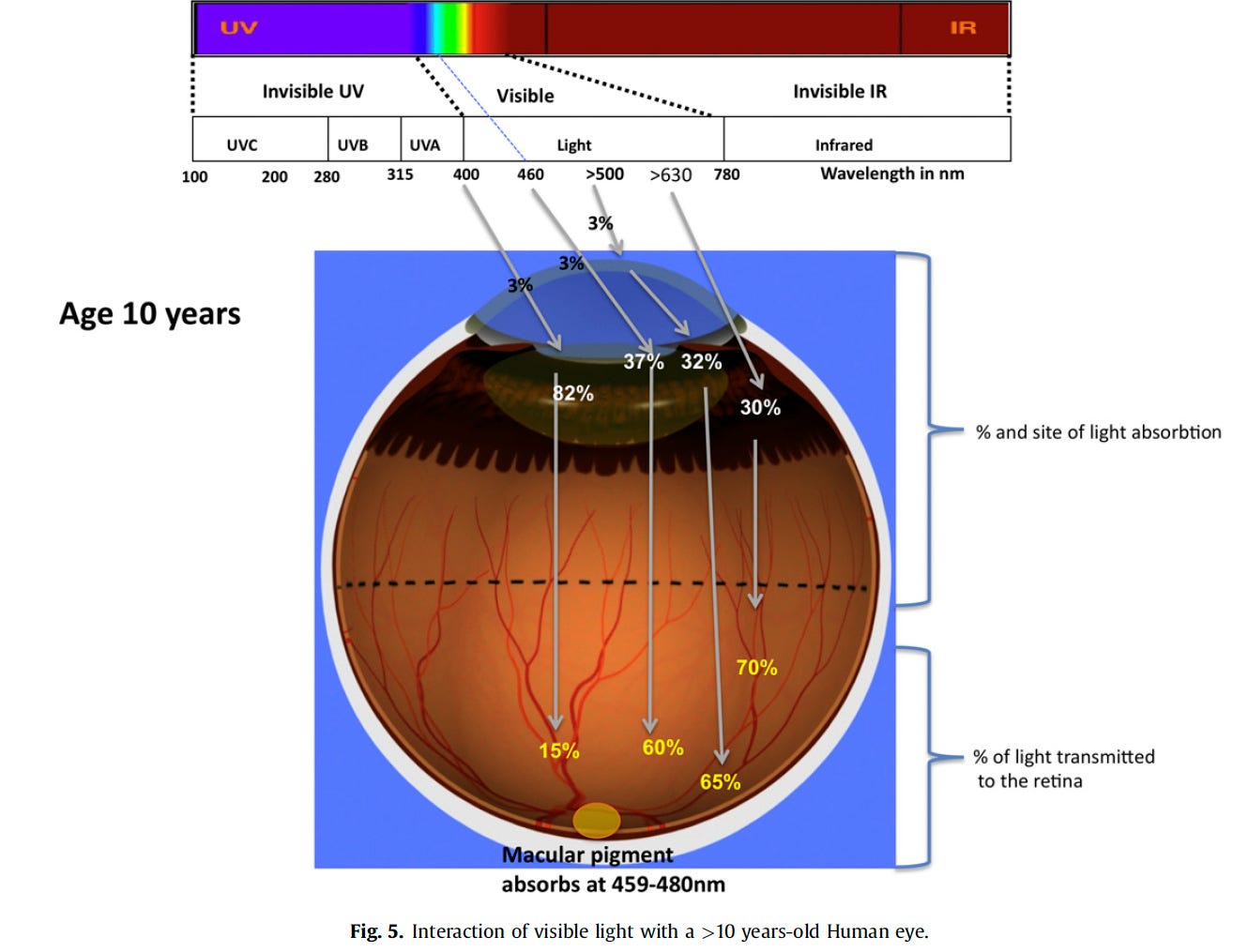
Children under 10 years of age absorb 60% more blue light into their retina as the lens of their eyes is not yet fully developed - link to study.
Blue light also scatters more easily than most other visible light, making it difficult for our eyes to focus. Instead, our eyes may digest blue light as poorly focused visual static. This reduction in contrast may make it more difficult for our eye to process blue light, contributing to eyestrain.11
How blue light contributes to diseases of the brain
Blue light dehydrates cells because it causes them to stop producing H20 from mitochondria, the engines of our cells.
Why is this important?
Neurons absorb and release water when firing. When H2O is missing in action so are neurological capabilities.12
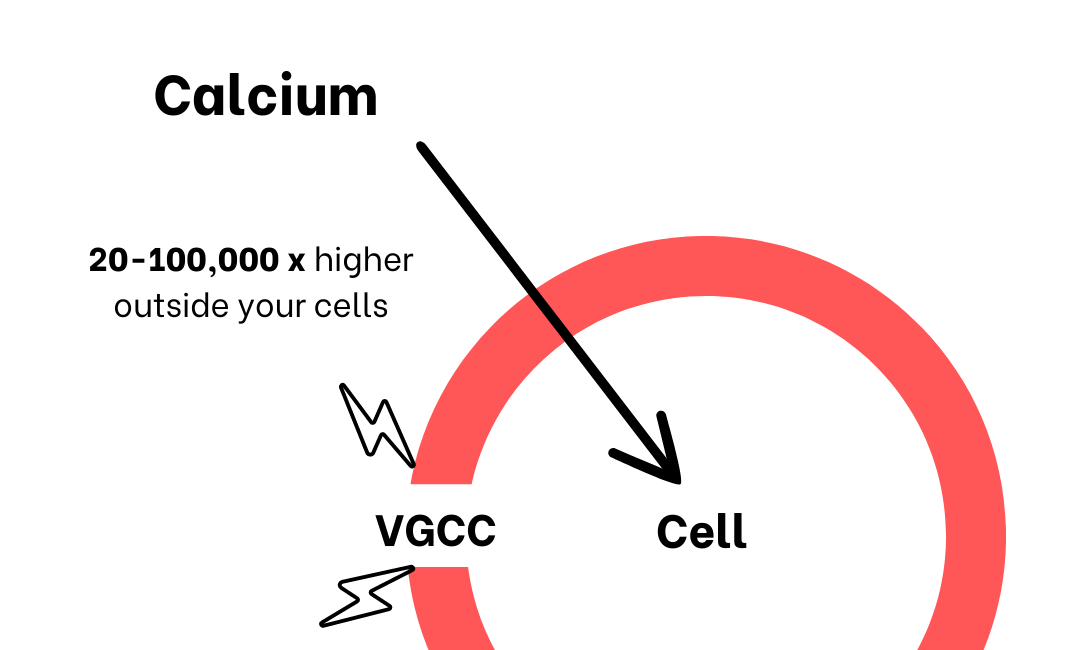
Our neurotransmitters (NT) such as dopamine, serotonin, GABA, all need calcium to work. Exposure to excessive blue light is also associated with calcium efflux in mitochondria. As calcium flows out of our mitochondria, and into our bloodstream, it causes problems with NT release.
EMFs from our devices and Wi-Fi also create an imbalance of calcium in our hearts by activating what are known as voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC):
Remember how blue light can affect our circadian rhythm by disrupting communication to our suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)?
When our SCN is out of rhythm, our brain becomes more susceptible to all kinds of disease, including Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, as our our cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can no longer flush out toxins effectively through our glymphatic system when we sleep, contributing to formation of amyloid plaques and misfolded proteins in our brain.13 Each night we undergo a type of oil change for our brain, and the mechanism that facilitates this is our very own electricity.
We recharge like a battery at night
We use a crucial amino acid called DHA to regenerate at night. DHA allows us to use our body’s internal DC (direct current) electric circuit to regenerate at night.14
Blue light destroys DHA everywhere in our tissues. As DHA levels decline, the inputs to the SCN from melanopsin photoreceptors also decline. We start to lose our ability to repair as a result.
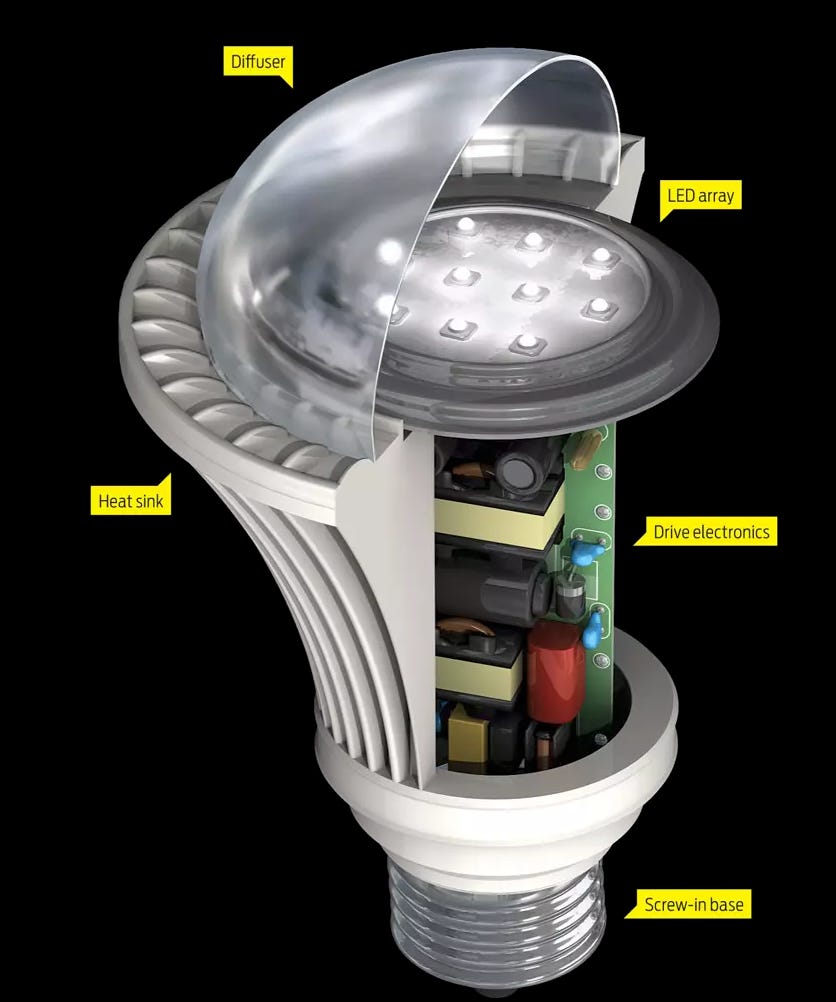
Anatomy of LEDs
We were told that LEDs are environmentally-friendly, however is this true?
Fluorescent bulbs are toxic enough, containing mercury vapor that can now be energized through radio transmitters called “electronic ballasts.”
LEDs bring it to another level, as many are now Wi-Fi enabled, adding a layer of nervous system disruption to our environment. I guess hitting a light switch was too hard?
LEDs have special electronic components that require toxic metals such as aluminum, gallium, indium and gallium phosphide, and indium gallium nitride in order to work. These components are often switch mode power supplies, which operate at ultrasonic frequencies15, and have a multitude of health impacts. The FCC rules also allow every energy efficient bulb to emit microwave radiaton at frequencies up to 1,000 MHz.
These bulbs clutter landfills, and the precious metals used to make their electronic components take much longer to degrade in our soils than the copper wire of standard incandescents.
The LED light above, which you can also turn on from your phone, is just one example. Our streets are also being littered with this type of light pollution with smartlights, which are actually way more of a computer and 5G surveillance system than they are a bulb.
To check out examples of smart lighting, and the misinformation campaign telling us they are safe, please see the following article:
Is energy really being saved by LEDs in our home?
In the summer, the heat given off by incandescent light bulbs is wasted and increases the demand for air conditioning.
“But in winter, we gain that cost back because the heat from light bulbs then warms our homes. When we lose that extra source of heat, we have to make up the difference by burning more oil and gas. In Canada, which gets virtually all electricity from hydro power, banning incandescent bulbs was a mistake.”
-Arthur Firstenberg, The Invisible Rainbow
It may be difficult to imagine that light bulbs alone could make such a difference in home heating, but for those of you who remember having your entire home run on incandescent can attest to the heat given off by each bulb.
Note: heating with incandescents is still less energy-efficient than heating our homes with a heatpump.
When we factor in the health hazards of LEDs vs. the added benefits of infrared light of incandescents, as well as halogen, it’s an easy choice.
Red light is the human-friendly choice of balance.
What are some other EMFs in our homes we may have failed to consider?
AC Electric Fields:
AC Magnetic Fields:
DC Electric Fields:
Where do we go from here?
There are a multitude of strategies we can employ. As a building biology advocate (BBA) who has studied EMFs, I can tell you that raising awareness is always the first step, followed by small actions that build up over time.
When night time hits, my home turns into a red-glowing spa. The only LEDs I have in my house are on my oven clock, and pressure-cooker, which I’ve covered up with a red translucent tape.
Regardless of 5G, cell towers, and satellites, the most ubiquitous form of EMF in our world today is blue light, and to an extent, we can all control that.
Why not start today?
I’m creating a course on EMF Basics & Ancestral Health
How can we measure DC electric fields in our environment?
What are electrocution hazards in our homes, like metal piping that hasn’t been bonded?
What are some other ways we can nourish the DC electric field of our body?
I’ll be covering these types of specifics, along with practical steps we can take to reduce EMFs in our daily lives, in the Wireless Health & Safety course I’m creating.
You are more powerful than you know.
Roman
The new 5G meter by Safe Living Technologies is out!
Consider becoming a paid subscriber!
You’ll have access to our monthly Q&A webinars, along with tools and nuggets of wisdom we’ve created to navigate this wacky wireless world.
Listen to our podcast - The Power Couple
We discuss how we:
Power ON with light
Power OFF our devices
Power thru our days with relationships that all start with - YOU.
New episodes each Friday:
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/519622
https://romanshapoval.substack.com/i/79596182/how-we-digest-light
https://www.patreon.com/DrJackKruse/posts?filters[search_query]=predator
Zimmerman S., Reite R. Melatonin and the Optics of the Human Body
https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250016
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/time-rethink-your-truth-sun-jack-kruse?published=t
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/blue-light-has-a-dark-side
https://www.melatonin-research.net/index.php/MR
https://jackkruse.com/the-dark-knight/
https://jackkruse.com/cpc-6-pseudotumor-cerebri/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1567724916302586
https://www.healthline.com/health/what-is-blue-light#risks-and-side-effects
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mrm.27473
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30377818/
Becker, R. The Body Electric. Harper Collins. 1985.
Firstenberg, A. The Invisible Rainbow. Chelsea Green Publishing. 2020.



















Nice article! Does your black Sub theme have anything to do with all this?
About
"Do you still think staying up watching Netflix until midnight with your biohacking blue-blocking glasses is a good idea?"
Do you mean to say the glasses won't help much? Just not sure. Anyway, I won't watch Netflix no matter what color they throw at me because the content will make my brain mush not just the light.
Thanks. Looks like you've learned a lot from Jack Kruse, as did I: https://youtu.be/d7qjh4BIGbc . Yes, UV works with infrared and other parts of the spectrum, and as you point out, they only test with artificial indoor UV in isolation. They block out the sunrise and sunset 90% of the time over here with their geoengineering. They are setting up more and more of their eerie purple LED lights over here. Wood stove infrared energy and candlelight are the best. They want to create a world where zombies survive shots and this plastic world.